Overview
Architecture Diagram
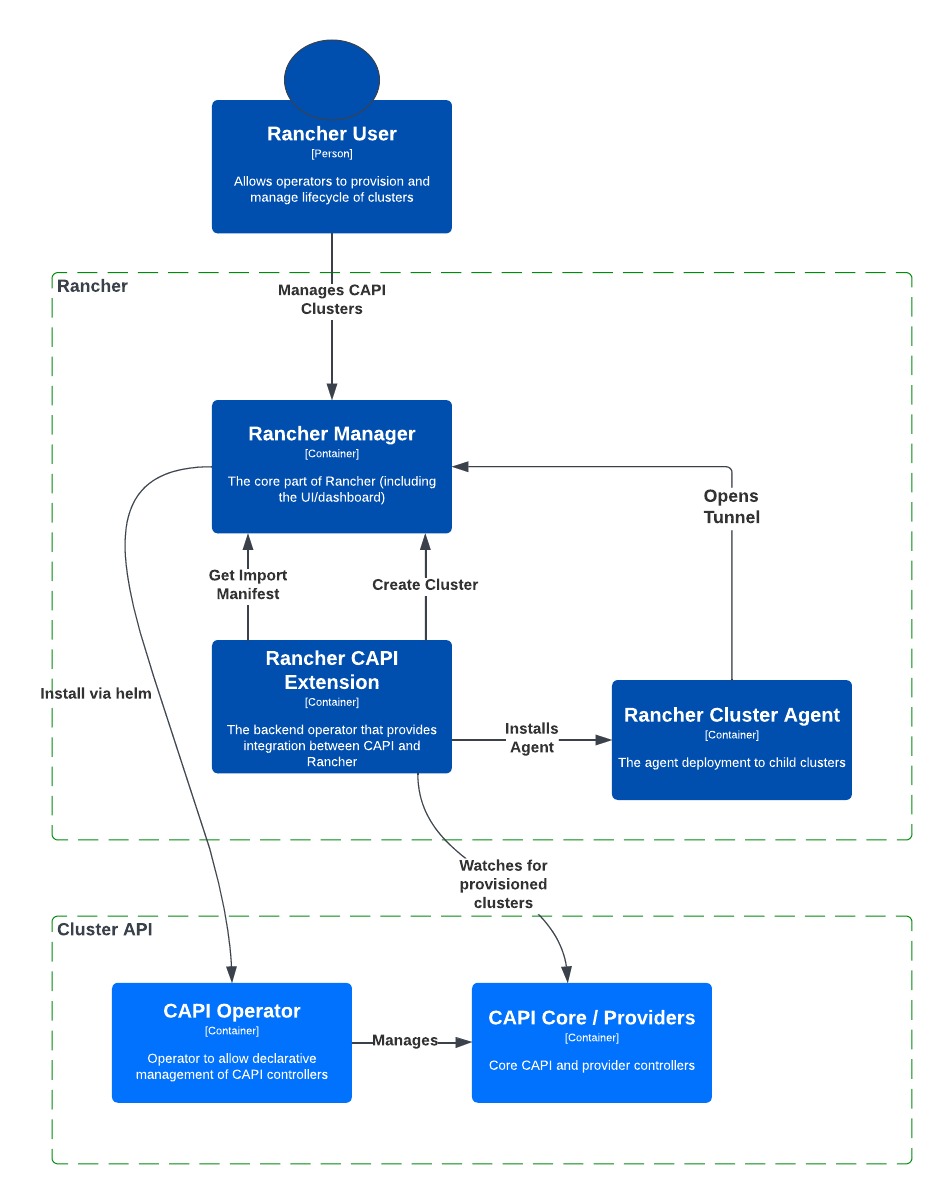
Below is a visual representation of the key components of Rancher Turtles and their relationship to Rancher and the Rancher Cluster Agent. Understanding these components is essential for gaining insights into how Rancher leverages the CAPI operator for cluster management.
Security
As defined by Supply-chain Levels for Software Artifacts (SLSA), SLSA is a set of incrementally adoptable guidelines for supply chain security, established by industry consensus. The specification set by SLSA is useful for both software producers and consumers: producers can follow SLSA’s guidelines to make their software supply chain more secure, and consumers can use SLSA to make decisions about whether to trust a software package.
Rancher Turtles meets SLSA Level 3 requirements as an appropriate hardened build platform, with consistent build processes, and provenance distribution. For more information, visit the Rancher Turtles Security document.
Prerequisites
Before installing Rancher Turtles in your Rancher environment, you must disable Rancher's embedded-cluster-api functionality. This also includes cleaning up Rancher-specific webhooks that otherwise would conflict with CAPI ones.
To simplify setting up Rancher for installing Rancher Turtles, the official Rancher Turtles Helm chart includes a pre-install hook that removes the following:
- Disables the
embedded-cluster-apifeature in Rancher. - Deletes the
mutating-webhook-configurationandvalidating-webhook-configurationwebhooks, as they are no longer needed.
These webhooks can be removed through the Rancher UI as well:
- In the upper left corner, click ☰ > Cluster Management.
- Select your local cluster.
- In the left-hand navigation menu, select More Resources > Admission.
- From the dropdown, select the Resource pages for
MutatingWebhookConfigurationandValidatingWebhookConfiguration. - On the respective Resource pages, click the ⋮ that are attached to the
mutating-webhook-configurationandvalidating-webhook-configurationwebhooks and select the Delete option.
The webhooks can also be accessed by entering the names of the webhooks into the Resource Search field.
The following kubectl commands can manually remove the necessary webhooks:
kubectl delete mutatingwebhookconfiguration.admissionregistration.k8s.io mutating-webhook-configuration
kubectl delete validatingwebhookconfigurations.admissionregistration.k8s.io validating-webhook-configuration
Use the following example to disable the embedded-cluster-api feature from the console:
- Create a
feature.yamlfile, withembedded-cluster-apiset to false:
apiVersion: management.cattle.io/v3
kind: Feature
metadata:
name: embedded-cluster-api
spec:
value: false
- Use
kubectlto apply thefeature.yamlfile to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f feature.yaml
Installing the Rancher Turtles Operator
You can install the Rancher Turtles operator via the Rancher UI, or with Helm. The first method is recommended for most environments.
If you already have the Cluster API (CAPI) Operator installed in your cluster, you must use the manual Helm installation method.
Installing via the Rancher UI
By adding the Turtles repository via the Rancher UI, Rancher can process the installation and configuration of the CAPI Extension.
- Click ☰. Under Explore Cluster in the left navigation menu, select local.
- In the left navigation menu of the Cluster Dashboard, select Apps > Repositories.
- Click Create to add a new repository.
- Enter the following:
- Name: turtles
- Index URL: https://rancher.github.io/turtles
- Wait until the new repository has a status of
Active. - In the left navigation menu, select Apps > Charts.
- Enter "turtles" into the search filter to find the Turtles chart.
- Click Rancher Turtles - the Cluster API Extension.
- Click Install > Next > Install.
This process uses the default values for the Helm chart, which are good for most installations. If your configuration requires overriding some of these defaults, you can either specify the values during installation from the Rancher UI or you can manually install the chart via Helm. For details about available values, see the Rancher Turtles Helm chart reference guide.
The installation may take a few minutes and after completing you can see the following new deployments in the cluster:
rancher-turtles-system/rancher-turtles-controller-managerrancher-turtles-system/rancher-turtles-cluster-api-operatorcapi-system/capi-controller-manager
Demo
This demo illustrates how to use the Rancher UI to install Rancher Turtles, create/import a CAPI cluster, and install monitoring on the cluster:
Installing via Helm
There are two ways to install Rancher Turtles with Helm, depending on whether you include the CAPI Operator as a dependency:
- Install Rancher Turtles with CAPI Operator as a dependency.
- Install Rancher Turtles without CAPI Operator.
The CAPI Operator is required for installing Rancher Turtles. You can choose whether you want to take care of this dependency yourself or let the Rancher Turtles Helm chart manage it for you. Installing Turtles as a dependency is simpler, but your best option depends on your specific configuration.
The CAPI Operator allows for handling the lifecycle of CAPI providers using a declarative approach, extending the capabilities of clusterctl. If you want to learn more about it, you can refer to Cluster API Operator book.
Installing Rancher Turtles with Cluster API (CAPI) Operator as a Helm dependency
- Add the Helm repository containing the
rancher-turtleschart as the first step in installation:
helm repo add turtles https://rancher.github.io/turtles
helm repo update
- As mentioned before, installing Rancher Turtles requires the CAPI Operator. The Helm chart can automatically install it with a minimal set of flags:
helm install rancher-turtles turtles/rancher-turtles --version <version> \
-n rancher-turtles-system \
--dependency-update \
--create-namespace --wait \
--timeout 180s
- This operation could take a few minutes and after completing you can review the installed controllers listed below:
rancher-turtles-controllercapi-operator
- If
cert-manageris already available in the cluster, disable its installation as a Rancher Turtles dependency. This prevents dependency conflicts:--set cluster-api-operator.cert-manager.enabled=false - For a list of Rancher Turtles versions, refer to the Turtles release page.
This is the basic, recommended configuration, which manages the creation of a secret containing the required CAPI feature flags (CLUSTER_TOPOLOGY, EXP_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_SET and EXP_MACHINE_POOL enabled) in the core provider namespace. These feature flags are required to enable additional CAPI functionality.
If you need to override the default behavior and use an existing secret (or add custom environment variables), you can pass the secret name Helm flag. In this case, as a user, you are in charge of managing the secret creation and its content, including enabling the minimum required features: CLUSTER_TOPOLOGY, EXP_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_SET and EXP_MACHINE_POOL.
helm install ...
# Passing secret name and namespace for additional environment variables
--set cluster-api-operator.cluster-api.configSecret.name=<secret-name>
The following is an example of a user-managed secret cluster-api-operator.cluster-api.configSecret.name=variables with CLUSTER_TOPOLOGY, EXP_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_SET and EXP_MACHINE_POOL feature flags set and an extra custom variable:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: variables
namespace: rancher-turtles-system
type: Opaque
stringData:
CLUSTER_TOPOLOGY: "true"
EXP_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_SET: "true"
EXP_MACHINE_POOL: "true"
CUSTOM_ENV_VAR: "false"
For detailed information on the values supported by the chart and their usage, refer to Helm chart options.
Installing Rancher Turtles without Cluster API (CAPI) Operator as a Helm dependency
Remember that if you opt for this installation option, you must manage the CAPI Operator installation yourself. You can follow the manual installation guide in the Rancher Turtles documentation for assistance.
- Add the Helm repository containing the
rancher-turtleschart as the first step in installation:
helm repo add turtles https://rancher.github.io/turtles
helm repo update
- Install the chart into the
rancher-turtles-systemnamespace:
helm install rancher-turtles turtles/rancher-turtles --version <version>
-n rancher-turtles-system
--set cluster-api-operator.enabled=false
--set cluster-api-operator.cluster-api.enabled=false
--create-namespace --wait
--dependency-update
The previous commands tell Helm to ignore installing cluster-api-operator as a dependency.
- This operation could take a few minutes and after completing you can review the installed controller listed below:
rancher-turtles-controller
Uninstalling Rancher Turtles
When installing Rancher Turtles in your Rancher environment, by default, Rancher Turtles enables the CAPI Operator cleanup. This includes cleaning up CAPI Operator specific webhooks and deployments that otherwise cause issues with Rancher provisioning.
To simplify uninstalling Rancher Turtles (via Rancher or Helm command), the official Rancher Turtles Helm chart includes a post-delete hook that removes the following:
- Deletes the
mutating-webhook-configurationandvalidating-webhook-configurationwebhooks that are no longer needed. - Deletes the CAPI
deploymentsthat are no longer needed.
To uninstall Rancher Turtles:
helm uninstall -n rancher-turtles-system rancher-turtles --cascade foreground --wait
This may take a few minutes to complete.
Remember that, if you use a different name for the installation or a different namespace, you may need to customize the command for your specific configuration.
After Rancher Turtles is uninstalled, Rancher's embedded-cluster-api feature must be re-enabled:
- Create a
feature.yamlfile, withembedded-cluster-apiset to true:
apiVersion: management.cattle.io/v3
kind: Feature
metadata:
name: embedded-cluster-api
spec:
value: true
- Use
kubectlto apply thefeature.yamlfile to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f feature.yaml